Understanding Maternity Insurance Coverage Limits
Understanding Maternity Insurance Coverage Limits

Maternity insurance coverage is an essential part of your health plan when you’re expecting a child. It helps cover the often significant costs associated with pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. Let’s break down what maternity insurance typically covers and the limits to those benefits.
Maternity Coverage: What’s Typically Included
Maternity benefits within most health insurance plans address the various stages of pregnancy:
Pre and Post-natal Care: This includes expenses like doctor’s visits, essential diagnostic tests (such as ultrasounds and blood tests), and prescribed medications for both the pregnancy and recovery period.

Delivery Charges: Covers the costs of both normal vaginal deliveries (NVD) and cesarean sections (C-section). This includes fees for the surgeon, anesthesia, labor room charges, and the hospital stay.

Hospitalization Costs: Maternity insurance covers room rent, boarding, nursing care, and medication expenses during a hospital stay related to childbirth.

Newborn Care: Some plans provide coverage for the newborn baby for a designated period, usually up to 90 days. This can include hospitalization costs if medically needed, as well as basic vaccinations and essential newborn care.
Important Note about Group Health Insurance: Group health insurance policies often cover newborns from day one, but typically only for hospitalization costs and observation. Specific benefits like immunization and general well-baby care might not fall under this coverage unless it’s clearly stated in the corporate plan.
Maternity Expenses in India: Understanding Costs and Trends

Maternity expenses are a significant concern for expectant parents in India. As childbirth involves both emotional and financial aspects, having adequate maternity coverage is essential. In this section, we delve into the average costs associated with normal deliveries and cesarean sections (C-sections) in India.
Average Cost of Normal Delivery
- According to a 2021 report by the National Health Accounts (NHA) of India, the average cost of a normal delivery in the country is approximately ₹41,000.
- However, it’s crucial to recognize that this figure can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Location: Costs may differ between urban and rural areas.
- Type of Hospital: Public hospitals, private hospitals, and maternity clinics have varying fee structures.
- Amenities: The level of comfort and amenities chosen by the parents impacts the overall cost.
Average Cost of C-Section (Cesarean) Delivery
- The same NHA report suggests that the average cost of a cesarean section (C-section) delivery in India is approximately ₹62,000.
- Similar to normal deliveries, the cost of a C-section can fluctuate based on various factors:
- Geographical Location: Urban centers tend to have higher costs.
- Hospital Infrastructure: Premium hospitals with advanced facilities may charge more.
Trends and Considerations
- Rising Costs: Over the years, maternity expenses have been steadily increasing due to inflation and advancements in medical technology.
- Insurance Coverage: Having maternity insurance helps mitigate the financial burden. However, policyholders should be aware of waiting periods and coverage limits.
- Antenatal Care: Regular prenatal check-ups and early planning contribute to better cost management.
Comparative Costs of Maternity Services Across India’s Metro and Non-Metro Cities
India’s tiered city system significantly influences the cost and availability of healthcare services. In this analysis, we delve into the average costs of maternity care across different city tiers, providing insights into the financial aspects of childbirth in India.
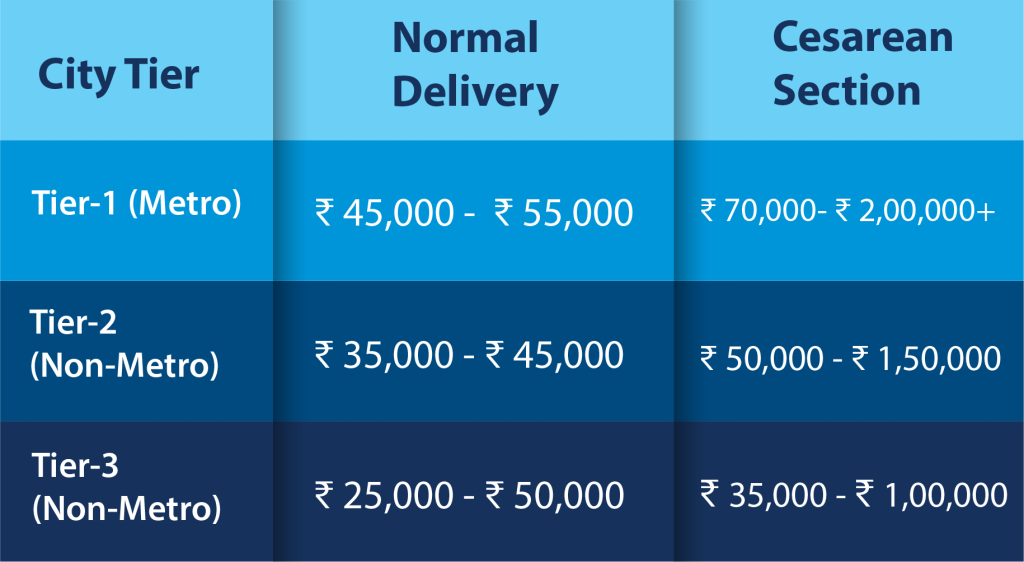
Key Characteristics:
- Tier-1 (Metro Cities):
▪ Specialized Healthcare: Metro cities house advanced hospitals and seasoned providers, contributing to higher average costs.
▪ Cesarean Prevalence: A greater frequency of Cesarean sections drives up overall expenses. - Tier-2 (Non-Metro Cities):
▪ Affordability and Quality: Non-metro cities strike a balance, offering comprehensive maternity services at relatively economical rates.
▪ Cost Advantage: Costs here are generally lower than in Tier-1 cities. - Tier-3 (Non-Metro Cities):
▪ Most Affordable: These cities cater to diverse financial capabilities, with a wider cost range due to service variability.
▪ Limited Specialization: While essential care is accessible, specialized services are less prevalent.
Financial Landscape of Maternity Coverage: Unveiling the Cost Structure
Understanding the factors that influence your maternity costs empowers you navigate the healthcare system effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the key players impacting your delivery expenses:
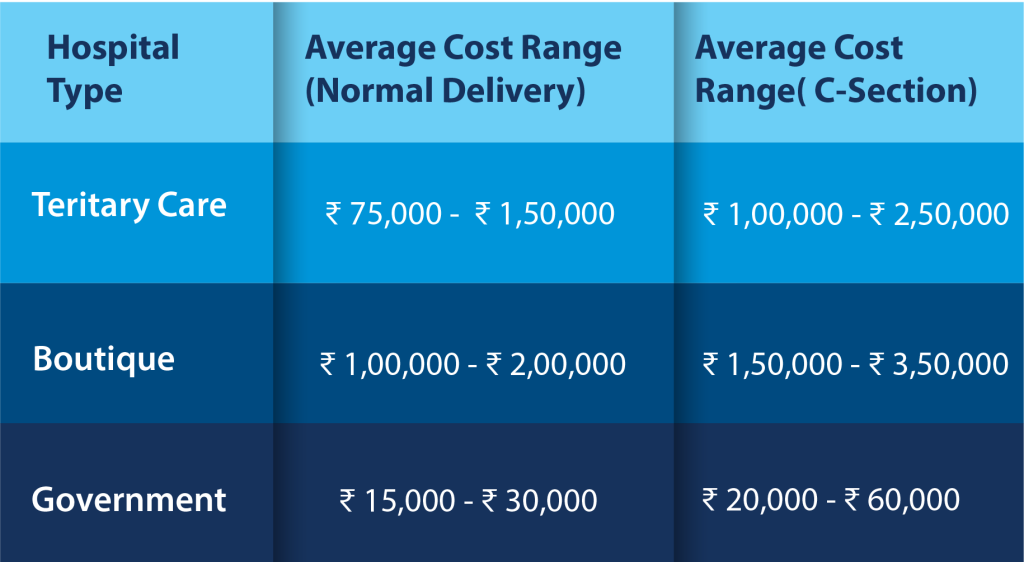
A. Hospital Type: A Spectrum of Options and Costs
● Tertiary Care Hospitals (Tier-1 Cities): Equipped with advanced technology and specialists, these hospitals offer the highest level of care but come with the highest price tag. Expect delivery costs to range from Rs. 75,000 to Rs. 2,00,000+ for both normal and C-section deliveries (depending on complexity).
● Boutique Hospitals (Tier-1 & Tier-2 Cities): Known for personalized care and luxurious amenities, boutique hospitals offer a comfortable birthing experience. However, due to their focus on smaller patient volumes and premium services, delivery costs in boutique hospitals can be even higher than tertiary care hospitals. Expect a range of Rs. 1,00,000 – Rs. 3,00,000+, with C-sections generally costing more.
● Government Hospitals (All Tiers): The most budget-friendly option, government hospitals offer essential maternity care. Normal deliveries can cost as low as Rs. 15,000, while C-sections might range from Rs. 25,000 to Rs. 60,000. However, longer wait times and limited amenities are common.
B. Healthcare Provider Fees: Expertise Comes at a Price
- Doctor’s Experience and Reputation: Expect fees to vary significantly. A renowned doctor in a Tier-1 city might charge Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 1,00,000+ for delivery, while a qualified doctor in a Tier-3 city could charge Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 50,000.
- Anesthesiologist Fees: Fees depend on experience and type of anesthesia used. Local anesthesia might cost around Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 15,000, while an epidural could range from Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 30,000.
- Pediatrician Fees: The initial newborn check-up typically falls between Rs. 2,000 – Rs. 5,000.
C. Specific Services Provided: Optimizing Care and Costs
The type of delivery, room selection, pain management choices, and any required newborn care services can significantly impact your final bill:
1. Type of Delivery:
- Normal Delivery: The most cost-effective option. Costs typically range from Rs. 15,000 – Rs. 50,000 in government hospitals and Rs. 75,000 – Rs. 1,50,000+ in private hospitals, depending on factors like doctor’s fees and room type.
- C-Section (Caesarean Section): A major surgery, significantly more expensive than a normal delivery. Costs can range from Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 1,00,000+ in government hospitals and Rs. 1,50,000 – Rs. 3,00,000+ in private hospitals, depending on factors like doctor’s experience, anesthesia type, and hospital stay duration.
2. Room Type:
Hospitals offer various room options, impacting your bill:
- Shared Room: Most economical option, with multiple beds in a single room. Offers basic amenities and privacy might be limited.
- Private Room: Provides a more comfortable and private birthing experience. Costs can be Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 15,000+ per night more than a shared room, depending on the amenities offered (single occupancy, attached bathroom, etc.).
- Suite: Most luxurious option, offering premium amenities like a living area and additional services. Costs significantly more than a private room but does’t covered under corporate health insurance plans
3. Pain Management:
The type of pain medication chosen during delivery influences costs:
- Local Anesthesia: Offers pain relief during specific procedures. Costs typically range from Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 15,000.
- Epidural: Provides continuous pain relief throughout labor. Generally more expensive than local anesthesia, costing Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 30,000+.
4. Newborn Care Services:
Additional services for your newborn can significantly increase costs. These might include:
- Phototherapy: Used to treat jaundice in newborns, costing around Rs. 5,000 – Rs. 10,000 per day.
- NICU Stay (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit): If your baby requires specialized care in the NICU, daily charges can range from Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 50,000+, depending on the level of care needed (ventilator support, medications, etc.).
Remember: These are estimated figures, and actual costs can vary. It’s crucial to research hospitals, compare costs, and discuss these options with your doctor beforehand to understand the associated costs and make choices based on your needs and budget.
Consider factors like your pregnancy health, potential risks, and pain tolerance when deciding on the type of delivery and pain management.
Important Factors for Choosing the Ideal Maternity Hospital with Corporate Health Insurance
Selecting the ideal hospital for your delivery in India is a crucial decision, especially when considering coverage health insurance. Here are key factors to consider during your selection process:
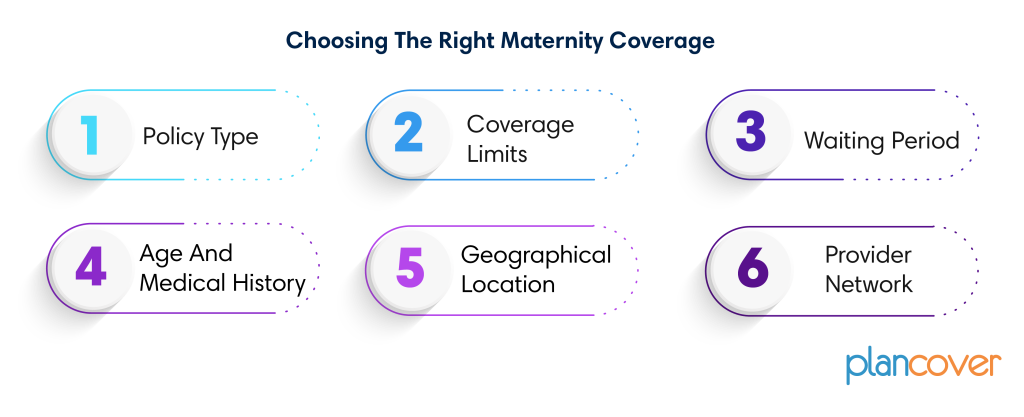
- Policy Type: Standalone maternity plans generally have fixed premiums while riders on existing health insurance policies might lead to an increase in the overall premium amount.
- Coverage Limits: Policies often impose sub-limits on specific expenses such as room rent, doctor’s fees, or diagnostic tests. Selecting plans with higher coverage limits naturally results in higher premiums.
- Waiting Period: Most policies have a waiting period before maternity benefits can be availed. This period can vary from a few months to several years. Policies with shorter waiting periods often come with higher premiums. However in GHI scheme Maternity are covered from day 1 but coverage is mere limited
- Age and Medical History: Premiums might be influenced by the age and medical history of the insured individual. Those with pre-existing medical conditions or older individuals may encounter higher premiums due to perceived higher risk.
- Geographical Location: Healthcare costs vary significantly across regions in India. Residents of metropolitan cities can expect higher medical expenses compared to those in smaller towns or rural areas. This variation is reflected in the cost structure of maternity coverage. Premiums might be higher in metro cities to account for the higher underlying medical costs.
- Provider Network: In-network hospitals within the insurer’s network often translate to lower out-of-pocket expenses compared to availing.
Choosing the Right Maternity Coverage: A Balancing Act
Selecting the most suitable maternity coverage option requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Individual Needs and Budget: Analyze your specific requirements regarding the extent of coverage desired and your financial capacity to shoulder the premiums.
- Family Planning Timeline: If you are planning a pregnancy in the near future, opting for a rider with a shorter waiting period might be more suitable. Standalone plans may be a better choice for those with a longer-term pregnancy timeline.
- Existing Health Insurance Coverage: If you already possess a health insurance policy, explore the option of adding a maternity rider before considering standalone plans.
- Policy Wording and Exclusions: Scrutinize the policy documents meticulously to understand the waiting period, sub-limits on specific expenses, coverage exclusions (pre-existing conditions, specific complications), and claim settlement procedures.
- Network Hospitals: Many insurance companies have tie-ups with specific hospitals or healthcare providers. Utilizing services within this network often translates to cashless hospitalization benefits and potentially lower out-of-pocket expenses.